Wiring a process instrument is quite hectic. Because, before you wire it you should know whether the transmitter is 2-wire, 3 wire or 4-wire. Also, the internal wiring of PLC analog input depends on the type of transmitter wiring.
Also, it is one of the most important selection criteria for process instruments as well.
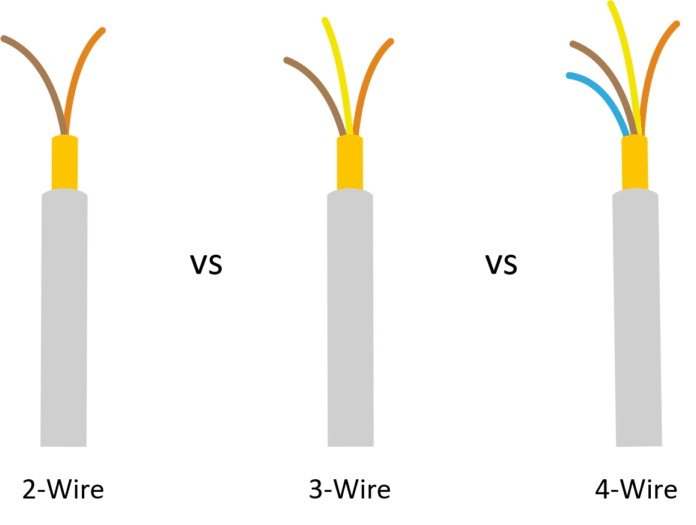
So in this article, I would tell you the difference between 2 wire 3wire and 4 wire transmitters wiring types along with their pros and cons.
2-Wire Transmitter
This is one of the simplest wiring types as it only has two wires. In this configuration supply power and 4-20 mA signal uses two-wire loop connections. Either the transmitter or the receiver would provide the power supply to the loop. However, a separate power supply is also available as an option.
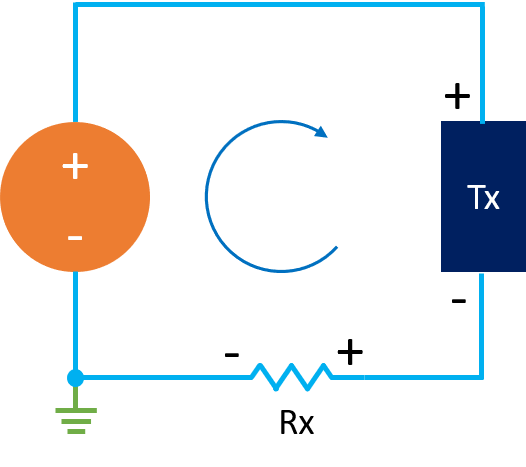
3-Wire Transmitter
The transmitter and receiver share common 0 V DC lines. 4-20 mA is supplied by the transmitter to the PLC module. 3rd wire is used to connect common 0 V DC.
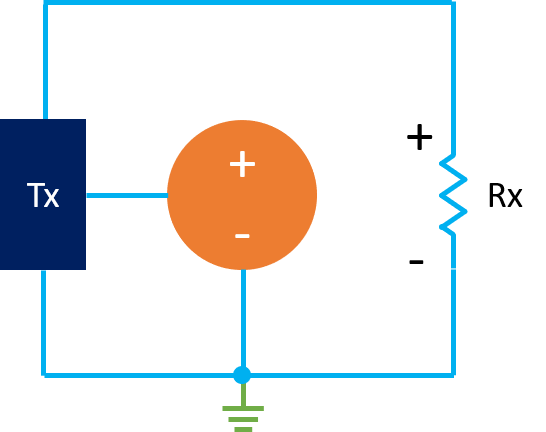
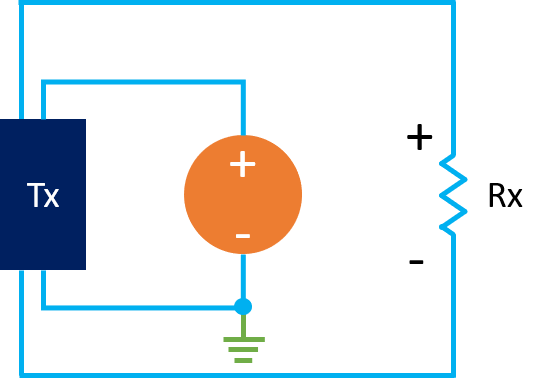
4-Wire Transmitter
The transmitter uses a separate 24 DC power supply. The 4-20 mA flows through two separate cables.






Good day! I just want to offer you a huge thumbs up for your excellent
information you’ve got here on this post. I will
be coming back to your blog for more stuffs like that.
Thank you